
| project name: | nb_drumcrow |
| project url: | https://github.com/entzmingerc/nb_drumcrow/ |
| author: | postsolarpunk |
| description: | norns mod that turns crow into a synth using nb |
| discussion url: | https://llllllll.co/t/nb-drumcrow-norns-mod-that-turns-crow-into-a-4-voice-synth/69066 |
| tags: | mod synth crow drum nb |
nb_drumcrow
This is a mod for monome norns that turns a monome crow into a synthesizer using nb.
Features:
- 4 synthesizers, one for each output of crow.
- Each output can be set to synthesize audio, gate/trigger, envelope, v/oct CV signal quantized to a scale, or convert the midi note from nb to a v/oct CV value.
- Trigger each output individually, round robin (4 voice polysynth), or all simultaneously.
- Use 2 crows connected via i2c to create an 8 voice version.
- Trigger 1 or more additional voices for paired operation (v/oct & gate pairs).
- Can be sequenced with teletype, with druid, with another crow, or with any norns script that supports nb.
- Each output has 3 cycling envelope modulation sources which map to 7 destinations.
- Bitcrusher waveshaper, saturation, PWM, global detune, vibrato, FM, and other fun experimental crow synthesis.
Requirements:
- monome crow
- monome norns (if using as an nb voice)
- install nb on your norns
- find a norns script that supports nb (nkria, pit orchisstra, arcologies, flora, cheat codes 2, washi, rudiments, dreamsequence, seeker, tetra, mosaic …)
- teletype: upload the update_loop.lua file to crow for standalone use
- a eurorack mixer of some kind to listen to the crow outputs
Tutorials and Demos

Tutorial covering installation and all parameters of nb_drumcrow when used as an nb voice.

Tutorial on how to use teletype to sequence nb_drumcrow with and without norns.
Exploration of the bitcrusher and waveshaping on nb_drumcrow.
video demo of nb_drumcrow as a bass synth.
video demo of nb_drumcrow in 8 voice mode.
Installation
1) Download this like you would any other script by typing ;install https://github.com/entzmingerc/nb_drumcrow into maiden.
2) Turn on the mod: navigate to SYSTEM > MODS > nb_drumcrow, turn enc3 to the right until you see a “+”. This tells norns to load the mod at the next power on.
3) Go to SYSTEM > RESTART, restart norns, then check your list of mods. It should have a dot “.” to the left of the name indicating the mod has been enabled.
4) Load a script that supports nb.
5) Go to the norns params menu and select drumcrow 1, 2, 3, or 4 from your list of nb voices.
6) Start playing notes with a norns script that uses nb.
Parameters
MODS Menu Settings
| Parameter | Description | Range | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| number of crows | one crow or two crows connected via i2c | 1, 2 | 1 |
| script start upload | whether or not to upload the code to crow automatically on script start | off, on | on |
These settings can be found in the SYSTEM > MODS > nb_drumcrow menu when the mod is enabled on norns. To prevent automatically uploading code from norns to crow when a norns script is loaded, set “script start upload” to off.
8 voice mode
nb_drumcrow uses 1 crow with 4 outputs or can use 2 crows and 8 outputs if the two crows are connected via i2c. To enable 8 voice mode, set the number of crows to 2 and restart norns. There will now be 8 voices to select from in the nb voice selector (drumcrow 1 - 8). After loading a script and sending the code to the first crow, disconnect the USB connection to the first crow and connect norns to the second crow. Then press resend code to crow to upload code to the second crow. Now, the second crow that is currently connected via USB to norns will be associated with drumcrow voices 1-4 and the first crow will be voices 5-8. This will not stay uploaded to crow if the power is turned off, so you’d need to do this each time you want to use 8 voices.
Instead, you can use druid to upload the file at nb_drumcrow/lib/update_loop.lua to the crow not connected via USB to norns so that nb_drumcrow runs when powered on for that crow. Then, the crow connected via USB to norns can have the code sent to it either automatically when you load a norns script if “script start upload” is on, or by using resend code to crow. Crows default to ii.address 1, so any command sent from norns to the USB connected crow for voices 5-8 is forwarded to “crow 1” using i2c.
Please note that 8 voice mode is not supported when using teletype. Only the 4 voice mode is supported when using teletype.
Global Settings
| Parameter | Description | Range | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| resend code to crow | (GLOBAL) reuploads audio engine code to run on crow | BUTTON | not pressed |
| param behavior | (GLOBAL) set this player or all players when changing a value | individual, all | individual |
| trigger behavior | (GLOBAL) controls what to do with note on trigger | individual, round robin, all | individual |
| global detune | (GLOBAL) multiplier to all channel frequencies, channel 1 frequency | -0.5, 1.0 | 0 |
| synth preset | selects which preset to load | see synth presets | init |
| load preset | loads the synth preset | BUTTON | not pressed |
Use resend code to crow to send code to crow to restart the sound engine. If you see “READY!” in maiden, then the upload has worked. The first time the mod is loaded on norns, all outputs will be set to the init preset. Whenever resend code to crow is pressed, it will upload the code then set all drumcrow nb voices to the current parameter values listed on norns. The default parameter values listed are the values of the init preset.
Param behavior can be set to “individual” or “all”. If set to individual, then any parameter value change will only apply to the drumcrow voice whose menu is being edited. If set to all, then any paramter value change is applied to all drumcrow voices at once. Trigger behavior controls what happens when a note is played for any drumcrow voice. Individual will play only the selected drumcrow voice, round robin will cycle through each of the 4 outputs of crow playing each output 1, 2, 3, 4, then 1, and all will play all 4 outputs at once with the same note. Use param behavior “all” with trigger behavior “round robin” to use all 4 outputs of crow as a 4 voice polyphonic synthesizer. Use param behavior “individual” and trigger behavior “individual” to use this as a drum machine to play each output independently. (GLOBAL) settings always apply their values to all drumcrow voices. Therefore, you can’t have two drumcrow voices with different trigger behaviors.
Global detune will offset the frequency of each drumcrow voice by a slight amount. At 1, frequencies for outputs 1 - 4 will be multiplied by x1, x2, x4, x8, and at -0.5 they are multiplied by x1, x0.5, x0.25, x0.125. Use very small values for chorus effects. Synth preset selects which preset to load. Load preset will load the selected preset. Use param behavior “all” when loading a preset to load the selected preset to all drumcrow voices.
Oscillator Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Range | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| synth shape | affects tone, sets voltage path between to() calls in ASL model | 1-9 | sine |
| synth model | different ASL models that are oscillating | 1-7 | var_saw |
| birdsong | transposition sequence, stepped each note on | see species | off |
| flock size | number of voices triggered during note on | 1-4 | 1 |
| midi note -> amp | converts midi note to amplitude for outputting v/oct | off, on | off |
| max freq | limits the maximum oscillator frequency | 0.01, 1 | 1 |
| transpose | offsets the midi note | -120, 120 | 120 |
| pulse width | functionality changes with ASL model | -1, 1 | 0 |
| pulse width 2 | functionality changes with ASL model | -10, 10 | 0 |
| ^^bitcrush (v/oct) | crow output scaling amount, volts per octave | -10, 60 | 0 |
| ^^mutate | multiplier of each value in corvus scale | -5, 5 | 1 |
| ^^corvus | scale to quantize output voltage to | see species | off (chromatic) |
| ^^amp limit pre-bit | limits amplitude before bitcrusher | ±0, ±1, ±5, ±10, ±20, ±40 | ±10 |
| splash | amount of randomness applied to the frequency | 0, 3 | 0 |
Synth shape selects the shape used to travel between voltages set by the ASL synth model (see synth shapes section). Synth model selects the ASL synth model (see synth models section). Each time a note is played, birdsong will step through the selected sequence and will add the value at its position in the sequence as a trasposition to the note being played. Flock size is the number of drumcrow voices triggered each time a note is played for this voice. For example, if drumcrow 2 is played, and flock size is 3, then it will play drumcrow 2, 3, and 4. This always increments positively and wraps around from 4 back to 1. Try using birdsong and flock size to create generative melodies. Midi note -> amp will convert the midi note played to amplitude. This is intended to be used with CV Pitch preset to convert the midi note to a constant voltage v/oct signal.
Max freq sets the maximum oscillator frequency (cyc) from 1% to 100%. All models are limited to 5919 Hz (midi note 114) and when using logarithmic and exponential shapes frequency is limited to 2793 Hz (midi note 101). Try using an LFO to create fake filter sweep sounds by modulating max freq, or increase the LFO cycle freq to create FM tones that interfere less with the requested note frequency. Transpose offsets the requested note by 1 half step per increment, so +12 would be 1 octave up. The parameters pulse width and pulse width 2 change behavior with each ASL model. Note that when using var_saw, pulse width is actually pulse width and pulse width 2 is not used. Bitcrush sets the v/oct amount of the crow quantizer. If bitcrush is less than or equal to 0, then no quantization is applied to the output. Mutate modifies the values of the scale used with the bitcrusher. Corvus is used to select which scale to use with the bitcrusher. If mutate is 1, then there is no change in the values of the scale.
Amp limit pre-bit limits the amplitude of the signal before the bitcrusher. Crow can only output values -5 V to +10 V, so any amplitudes requested will be hard clipped on the output. Splash adds a random amount to the oscillator frequency, use a small value for a chorus like effect, or a large value for a deteriorated signal.
Envelope Parameters (Amp, LFO, Note)
| Parameter | Description | Range | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| amp -> max freq | modulation depth of maximum frequency | -1, 1 | 0 |
| amp -> osc note | modulation depth of oscillator frequency | -5, 5 | 0 |
| amp -> amplitude | modulation depth of amplitude | -5, 5 | 1 for amp only |
| amp -> pulse width | modulation depth of pulse width | -2, 2 | 0 |
| amp -> pulse width 2 | modulation depth of pulse width 2 | -10, 10 | 0 |
| amp -> bitcrush | modulation depth of bitcrush | -10, 60 | 0 |
| amp -> mutate | modulation depth of bitcrush | -10, 10 | 0 |
| amp cycle freq | how quickly the envelope rises and falls | 0.1, 200 | various |
| amp symmetry | ratio rise time to fall time | -1, 1 | amp & note: -1, lfo 0 |
| amp curve | shape of rise & fall, -5 square, 0 linear, 5 exponential | -5, 5 | amp 1, lfo 0, note 4 |
| amp loop | if on: envelope begins again after fall is complete | off, on | amp & note: off, lfo on |
| amp reset | if on: envelope resets from the start of rise during note on | off, on | amp & note: on, lfo off |
The 3 envelopes, amp, lfo, and note are functionally identical, but have different values when loading the init preset. amp modulates amplitude by 1.0, loop is off, and reset is on. lfo loop is on and reset is off. note loop is off and reset is on. Each envelope has the same set of modulation targets, modulation depth ranges, and envelope parameters. The modulation depth adds to the current value of the parameter it is modulating (except for amplitude). For example: pulse width at 0.4, lfo -> pulse width modulation depth at 0.2, then you’ll hear pulse width modulate back and forth between 0.4 and 0.6. For modulation depth -0.8, you’d hear 0.4 to -0.4. For amplitude, if amplitude modulation depth is 0 for all envelopes then you’ll hear silence. Amplitude modulation depth of 1.0 results in a +/- 5 V range. Crow hard clips voltages below -5 and above +10, so higher amplitude modulation depths can be used to saturate oscillators.
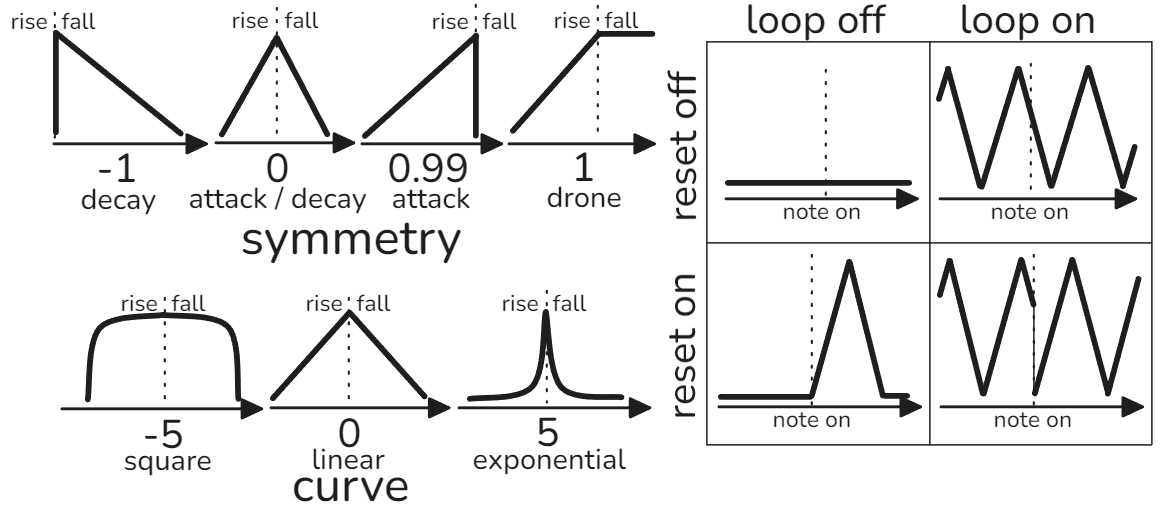
Cycle freq sets the frequency wavelength, smaller values result in longer times, higher values are shorter times. Symmetry controls ratio between rise time and fall time. At -1, rise time is 0%, fall time is 100%. At 0.99, rise time is 100% and fall time is 0%. At 1, the fall stage doesn’t trigger and it will stay at the maximum value. Curve controls the response curve of the envelope from a logarithmic shape at -5, linear shape at 0, and an exponential shape at +5. Loop controls whether or not the rise stage is triggered again at the end of the fall stage. Reset controls whether or not the envelope resets to the start of the rise stage when a note is played. Envelopes can only be reset if in the fall stage of the envelope. Thus, envelopes will ignore resets if the envelope is still rising. If reset is off then the envelope will not be reset.
Bitcrusher Operation
| Corvus Species | Scale |
|---|---|
| off | (chromatic) |
| cornix | 0, 2, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11 (major) |
| orru | 0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 9, 10 (minor) |
| kubaryi | 0, 3, 5, 7, 10, 12, 15 (minor pentatonic) |
| corone | 0, 11, 9, 7, 5, 4, 2 |
| levaillantii | 0, 7, 12, 5, 0, 5, 12 |
| culminatus | 0, 7, 12, 24, -12, 0, 12 |
| edithae | 0, 24, 5, 22, 7, 19, 12 |
| florensis | 0, 17, -17, 0, -17, 17, 12 |
| brachyrhynchos | 0, -7, -10, 12, 24, 17, 12 |
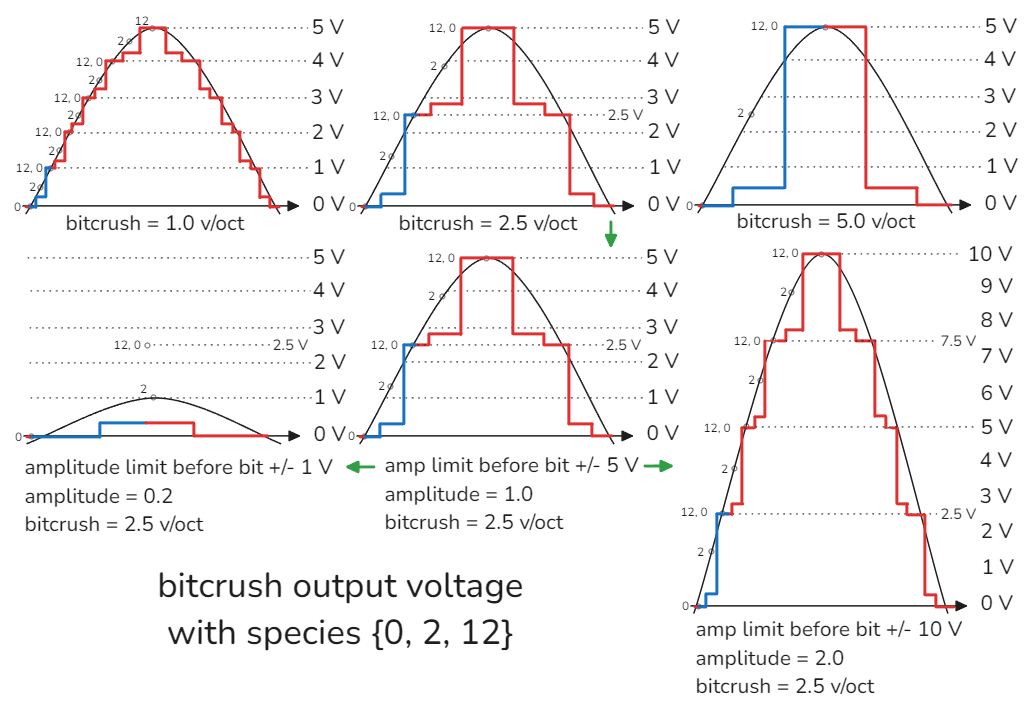
The bitcrusher uses crow output quantizer to do distortion. A bitcrush value of 1.0 results in 1 volt per octave. The output voltage will then be quantized to the scale selected with corvus. The first 4 scales are chromatic, major, minor, and minor pentatonic. Scale values can be out of order to create arpeggios and can have note values outside the range 0 - 12.
Each octave is divided evenly into a number of sections equal to the number of notes in the scale. There are 7 values per scale. For higher values of bitcrush, the shape of the scale is applied to the larger range of voltage. For example, the shape of the stairstep voltage waveform that occurs between 0V and 1V when quantizing to a major scale for a bitcrush value of 1 v/oct would be stretched across the voltage range 0V and 5V if bitcrush is set to 5 v/oct. For this reason, a variety of scales can be used to significantly change the tone of the bitcrushing.
An amplitude modulation depth of 1 results in an amplitude of ±5 V. Crow hardware is limited to -5 V and 10 V. The amp limit pre-bit parameter sets the maximum range of voltage that drumcrow will request. It defaults to ±10 V. By increasing the amplitude modulation depth to 2, you can increase the oscillator amplitude to ±10 V and crow will clip the bottom part of the waveform for a more overdriven tone. Any values in a corvus scale above 12 or below 0 will map to voltages outside of the octave range. With larger bitcrush and mutate values, this can generate much louder outputs signals. Varying amplitude and bitcrush values between 0 and 5 can generate a lot of varied distortion tones.
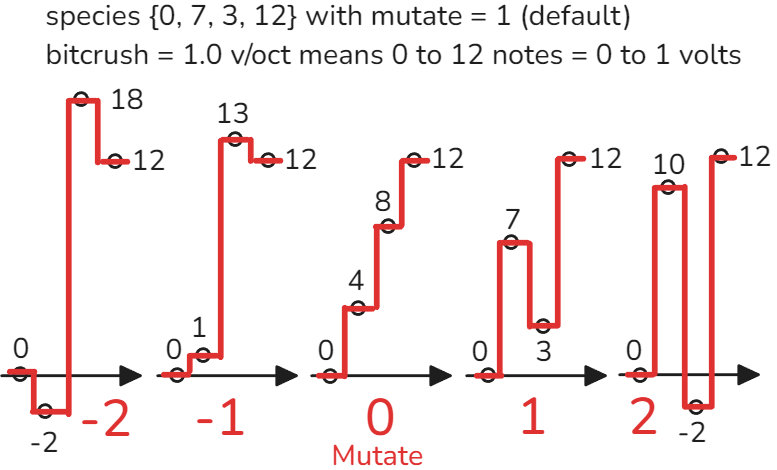
Mutate is used with bitcrush and corvus. Mutate will multiply all values of the corvus species scale up to a value of +/- 24. At mutate = 1, the values of the corvus scale are unchanged. At mutate = 0, the scale values are evenly distributed across the v/oct range. If mutate multiplies a scale value to above 24, it will start to decrease negatively below 24 by 4 times the rate. Similarly values below -24 will increase positively at 4 times the rate. This creates a lot of variation in the distortion tone when using high mutate values or when modulating mutate. Modulating between -1 and +1 there will be a small change in tone but not much change in distortion. Modulating to values above 1 or below -1 will give dramatically more distortion and interesting tones. Try using LFO to slowly modulate mutate to hear “wavetable” type tones.
Synth shapes logarithmic and exponential shapes have unique mutate behavior. Usually the temperament of the crow quantizer is 12, but when using logarithmic or exponential shapes, temperament is multiplied by the absolute value of mutate. Mutate will not modulate the corvus scale values when using logarithmic and exponential shapes. When mutate approaches zero, spike in distortion occurs as the temperament of the quantizer approaches 0. Try modulating mutate through 0 to hear distortion amount swell in and out.
Synth Shapes
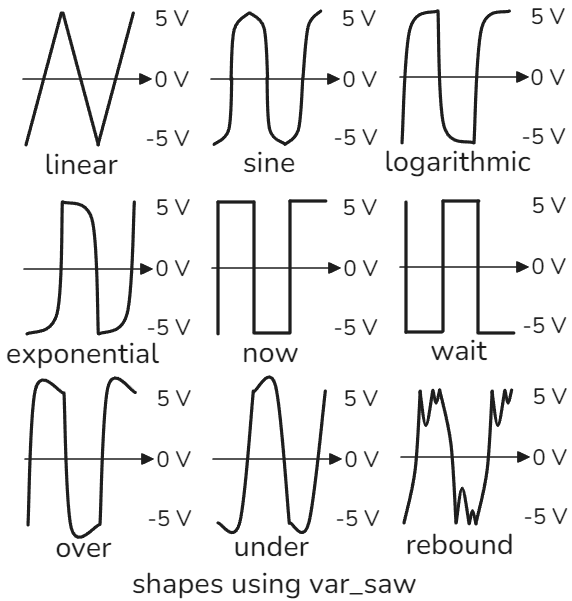
| Shapes | Description |
|---|---|
| linear | triangle, saw, connect the dots /\/ |
| sine | sine, looks like half a sine wave (default) |
| logarithmic | fast rise, slow settle |
| exponential | slow rise, fast settle |
| now | square, go instantly to the destination then wait |
| wait | square, wait at the current level, then go to the destination |
| over | move toward the destination and overshoot, before landing |
| under | move away from the destination, then smoothly ramp up |
| rebound | emulate a bouncing ball toward the destination |
These are the shapes from the crow reference. These are also known as “easing functions”. Using the var_saw synth model in the init preset, it’s easy to hear how shape affects the tone of the oscillator. Linear is a triangle wave, and by setting pulse width to +1 or -1 it can be turned into sawtooth wave. Sine is a sine wave. Now and wait are both square waves but have opposite polarity. I like rebound because introduces higher frequency components with the extra bounces in the waveform.
The var_saw ASL model can be turned into a constant positive voltage source using the “now” shape and pulse width set to 1. It can also be set as constant negative voltage source if pulse width is set to -1. Then, using the internal envelopes, amplitude can be modulated to create CV for triggers, envelopes, and v/oct signals. Synth shape significantly affects the tone of each ASL model and as a results also affects the sound of the bitcrusher.
Synth Models
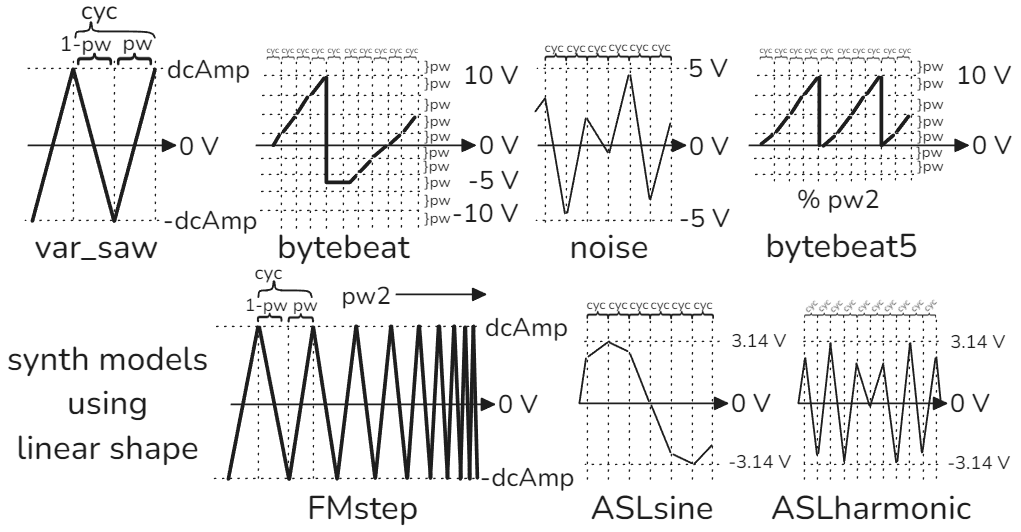
| Dyns | Description |
|---|---|
| dcAmp | Controls amplitude of the voltage |
| cyc | Controls update rate of the ASL loop |
| pw | pulse width, function changes with each ASL model |
| pw2 | pulse width 2, function changes with each ASL model |
Here are the dynamic variables used in the ASL models for each synth model. Each drumcrow oscillator must have a dyn{dcAmp=0} in its ASL model. Other dyns like cyc, pw, and pw2 are used as well to create the ASL models. These are the parameters being updated by the 3 modulation envelopes. Each ASL model is built around the loop{
var_saw
loop{
to( dyn{dcAmp=0}, dyn{cyc=1/440} * dyn{pw=1/2} , shape),
to(0-dyn{dcAmp=0}, dyn{cyc=1/440} * (1-dyn{pw=1/2}), shape)
}
To understand drumcrow is to understand var_saw. This is the default ASL model. It’s an LFO with pulse width and dynamic variables. Use shape to adjust waveform: linear is triangle, sine is sine, now or wait is square. Select any shape 1-9 to hear different tones. A pulse width value of 1 will result in a time of 0 sec for the second to{} in the ASL model, thus it will only output a constant positive voltage. Similarly, if pulse width is -1 then it will be a negative voltage.
bytebeat
loop{
to(dyn{x=1}:step(dyn{pw=1}):wrap(-10,10) * dyn{dcAmp=0}, dyn{cyc=1}, shape)
}
Output voltage is stepped by pw each loop and wrapped between -10 … 10. Crow hardware limit is -5 to +10V. cyc determines how often the ASL model loops. pw determines how much the voltage changes each time the ASL loops. Thus, both pw and cyc affect the resulting oscillation frequency. pw is calculated by multiplying the pulse width and pulse width 2 param values.
noise
loop{
to(dyn{x=1}:mul(dyn{pw2=1}):step(dyn{pw=1}):wrap(-5,5) * dyn{dcAmp=0}, dyn{cyc=1}, shape)
}
This is an LCG used to create a sequence of pseudorandom numbers. This implements the equation: x(n+1) = ((x * pw2) + pw) % 10. Set pulse width to 0.3 and pulse width 2 to a value around 3 to get some noise. Set transpose to a higher value to get higher frequency noise. Small positive values of both pw and pw2 can yield some interesting sounds near zero. Use short amplitude envelope cycle times (5-10) for high hats and snares. Set transpose to a lower value for a stream of random CV voltages. Use synth shape “now” for stepped random, “linear” for slewed random, or any other shape for a random sequence.
FMstep
loop{
to( dyn{dcAmp=0}, dyn{x=1}:step(dyn{pw2=1}):wrap(1,2) * dyn{cyc=1} * dyn{pw=1}, shape),
to(0-dyn{dcAmp=0}, dyn{x=1} * dyn{cyc=1} * (1-dyn{pw=1}), shape)
}
This expands the var_saw model to multiply cyc by x that sweeps between 1 and 2 at a speed set by pulse width 2. Low pulse width 2 values modulate the frequency slowly, high pulse width 2 values results in a more FM type sound.
ASLsine
loop{
to((dyn{x=0}:step(dyn{pw=0.314}):wrap(-3.14,3.14) + 0.101321 * dyn{x=0} * dyn{x=0} * dyn{x=0}) * dyn{dcAmp=0}, dyn{cyc=1}, shape)
}
This is a root-product sine wave approximation y = x + 0.101321(x)^3. The var_saw model creates a waveform by picking two voltage points to move between. If we wanted to step through a custom waveform, we would have to make 100 ASL stages and step through them all. Instead, we can loop one ASL stage, and step x by pulse width and wrap it between -pi and +pi. This roughly traces out a sine wave. x is stepped each time it’s referenced in the ASL model. The time it takes to step x to its next value is determined by cyc.
ASLharmonic
loop{
to((dyn{x=0}:step(dyn{pw=1}):mul(-1):wrap(-3.14,3.14) + 0.101321 * dyn{x=0} * dyn{x=0} * dyn{x=0}) * dyn{dcAmp=0}, dyn{cyc=1}, shape)
}
Same as ASLsine but we add a mul(-1) to x so each time x is called, the polarity flips. Slightly more chaotic, try exploring pulse width 2 values to hear different tones.
bytebeat5
loop{
to(dyn{x=0}:step(dyn{pw=0.1}):wrap(0, 10) % dyn{pw2=1} * dyn{dcAmp=0}, dyn{cyc=1}, shape)
}
Another bytebeat model. The mutator wrap(0, 10) means it will only output positive voltage unless amplitude is modulated negatively by the envelopes. Pulse width sets the step rate. Pulse width 2 sets the modulo range. cyc is the “sample rate” of the bytebeat shape.
Synth Presets
| Preset | Description |
|---|---|
| init | Sine wave oscillator with decay envelope |
| kick | Basic synth kick drum, useful for bass patches too |
| snare | Digital noise snare drum |
| hihat | Short noise pluck |
| CV trigger | CV gate / trigger, use amp cycle freq for gate length |
| CV envelope | rise / fall envelope using all 3 envelopes |
| CV scale | voltages quantized to 1 v/oct |
In the param menu, navigate to synth preset to select the preset you’d like to load. Then navigate to load preset and press KEY 3 to load the selected preset. The init preset is a sine wave oscillator using var_saw with a short decay envelope oscillating between +/- 5 V. Init is the default preset loaded to all outputs. Kick preset uses rebound shape, var_saw model, transposes down -24 steps, and utilizes the note envelope to quickly sweep the oscillator frequency from high to low emulating a kick drum sound. Snare and hihat preset both use the noise model and have short amplitude decay envelopes.
The CV presets allow drumcrow to be used as a CV source. Each utilizes var_saw with a pulse width of 1 to create a constant voltage output, then uses the envelopes to modulate the amplitude of the synth model. CV Trigger is set up to be a short square trigger or gate if the amp cycle freq is lengthened. CV Envelope is a rise / fall envelope. CV Scale sets bitcrush to 1 v/oct and maps the midi note to the amplitude of the synth model. All 3 envelopes can be used simultaenously for making various modulation signals. Try combining looping envelopes each modulating amplitude at different rates using CV Scale to create quantized chromatic lfos, or pick a scale to quantize to using corvus.
Teletype Operation
Teletype can sequence notes and set parameters on nb_drumcrow if crow is connected to teletype via i2c. Sequencing with teletype only supports the 4 voice mode with 1 crow connected. Crow also will need the update_loop.lua file uploaded to it. To do this, connect crow to your computer via USB. Download this GitHub repo to your computer then navigate to the folder wherever the nb_drumcrow/lib/update_loop.lua file is. Launch druid and upload the update_loop.lua file to your crow. Now, nb_drumcrow will be running whenever the modular case is powered on.
The only teletype OP needed is CROW.C4. Many parameters on nb_drumcrow require decimal values, but teletype can only send integers over i2c. To account for this, each value sent by teletype should be mulitplied by 100. When nb_drumcrow receives a parameter value from teletype, it will divide it by 100. This specifically applies only to parameter values and velocity. For example, if you want to set pulse width to 0.5, on teletype you’d send a value of 50. You could use the teletype command CROW.C4 2 1 4 50 which (2) sets a parameter value, (1) selects output 1, (4) selects pulse width, and (50) is the value sent by teletype which is divided by 100 on nb_drumcrow and results in 0.5.
If you connect a norns to crow, crow will stop running the uploaded script and listen for instructions from norns. Load a script that supports nb and resend code to crow if you have script start upload set to off to send update_loop.lua to run on crow. Once this is running, crow can now receive commands from teletype again, and the norns parameters menu can be used to edit parameter values on nb_drumcrow. If using norns to run update_loop.lua on crow, it isn’t necessary to upload the update_loop.lua file to crow using druid, but you’ll need to send the code from norns to crow each time you power on your modular case.
When playing notes from teletype, flock size and trigger behavior have no effect because the triggering logic for these parameters is done by the norns mod and not on crow. There is no way to load a preset from teletype either, only from norns. Make your own presets using teletype scenes and I. You can play notes and edit parameters simultaneously from both norns and teletype.
CROW.C4 x y z t
x is function: 1, 2, or 3
x = 1: Note On!
y is crow output (1, 2, 3, 4)
z is note (0 - 127)
t is velocity (multiply desired value by 100)
Play note 60 with velocity 1 on output 2: CROW.C4 1 2 60 100
x = 2: Set Parameter Value!
y is crow output (1, 2, 3, 4)
z is parameter index (1 - 56, table below)
t is parameter value (multiply desired value by 100)
Set amp cycle freq to 0.5 on output 3: CROW.C4 2 3 14 50
x = 3: Set Synth Model and Shape!
y is crow output (1, 2, 3, 4)
z is synth model (1 - 7)
t is synth shape (1 - 9)
Set synth model bytebeat and shape to linear on output 1: CROW.C4 3 1 2 1
Here is the list of parameter indices when setting a parameter value (x = 2).
| osc | amp | lfo | note |
|---|---|---|---|
| global detune = 56 | amp -> max freq = 8 | lfo -> max freq = 19 | note -> max freq = 30 |
| synth shape = 43 | amp -> osc note = 9 | lfo -> osc note = 20 | note -> osc note = 31 |
| synth model = 42 | amp -> amplitude = 10 | lfo -> amplitude = 21 | note -> amplitude = 32 |
| birdsong = 50 | amp -> pulse width = 11 | lfo -> pulse width = 22 | note -> pulse width = 33 |
| flock size = 51 | amp -> pwlse width 2 = 12 | lfo -> pwlse width 2 = 23 | note -> pwlse width 2 = 34 |
| midi note -> amp = 48 | amp -> bitcrush = 13 | lfo -> bitcrush = 24 | note -> bitcrush = 35 |
| max freq = 1 | amp -> mutate = 53 | lfo -> mutate = 54 | note -> mutate = 55 |
| note = 2 (hidden) | amp cycle freq = 14 | lfo cycle freq = 25 | note cycle freq = 36 |
| amplitude = 3 (hidden) | amp symmetry = 15 | lfo symmetry = 26 | note symmetry = 37 |
| transpose = 41 | amp curve = 16 | lfo curve = 27 | note curve = 38 |
| pulse width = 4 | amp loop = 17 | lfo loop = 28 | note loop = 39 |
| pulse width 2 = 5 | amp reset = 44 | lfo reset = 45 | note reset = 46 |
| ^^bitcrush (v/oct) = 6 | amp phase = 18 (hidden) | lfo phase = 29 (hidden) | note phase = 40 (hidden) |
| ^^mutuate = 52 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ^^corvus = 47 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ^^amp limit pre-bit = 49 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| splash = 7 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Druid Operation (or another crow?)
Similar to teletype operation, using druid you can call the ii.self.call4(a, b, c, d) function directly on a crow that has update_loop.lua uploaded to it. This is same set of functions and arguments described in the teletype operation section for CROW.C4 x y z t. It would be necessary to multiply d by 100 when setting a parameter value or velocity. It’s also possible to use druid and a text editor to livecode one crow which sequences another crow with update_loop.lua uploaded to it. You could do this by calling ii.crow[1].call4(a, b, c, d) on the first crow to play notes and set parameter values on the second crow with update_loop.lua uploaded to it.